
Get patients started on Mounjaro1
The Mounjaro experience, designed for patients like Julia1: not to A1C goal on metformin, struggling to lose excess weight despite her efforts with diet and exercise

Actor portrayal of an adult woman with type 2 diabetes
Ready to prescribe Mounjaro?
How to Prescribe Mounjaro
Help get patients started on Mounjaro1
Start

Provide patients with a
1-month* 2.5-mg starting
dose prescription
Prescribe
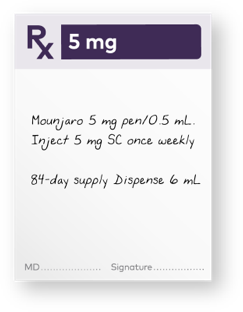
After 4 weeks on the 2.5 mg dose, provide patients with a 1-month* or 3-month† 5.0-mg prescription
Activate

Help your eligible patients save on Mounjaro
For eligible, commercially insured patients with Mounjaro coverage, Governmental beneficiaries excluded, terms and conditions apply
Image depicting how to prescribe Mounjaro. Starting Dose: provide patients with a 1-month 2.5-mg starting dose. Prescribe: After 4 weeks on the 2.5 mg dose, provide patients with a 1 - month* 2.5 mg prescription. Access: See HCP formulary access and top plans by clicking LEARN MORE. Activate: Help your patients save on Mounjaro. For eligible, commercially insured patients with Mounjaro coverage. Governmental beneficiaries excluded, terms and conditions apply.
Prior authorizations are common for the incretin class. Get tips for Prior Authorization Submission Process.
*One month is defined as 28 days and 4 pens.
†Three months is defined as 84 days and up to 12 pens.
The 2.5-mg dose is for treatment initiation and is not intended for glycemic control.
See Savings Card Terms and Conditions
2.5-mg dose NDC: 0002-1506-80; 5-mg dose NDC: 0002-1495-80l
How to Dose Mounjaro
Multiple doses for customizable glycemic control1‡
START THE EXPERIENCE
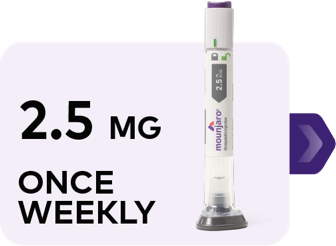
Starting dose (for 4 weeks)
MONTH 1
CONTINUE THE EXPERIENCE

For at least 4 weeks
MONTH 2
IF ADDITIONAL GLYCEMIC CONTROL IS NEEDED

For at least 4 weeks

For at least 4 weeks

For at least 4 weeks
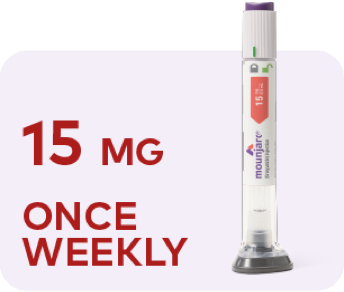
Maximum dose
Image depicting escalation of Mounjaro. Starting dose is 2.5 mg once weekly for 4 weeks. Continue to 5 mg once weekly for at least 4 weeks. If additional glycemic control is needed, dose can be increased to 7.5 mg once weekly for at least 4 weeks, then 10 mg once weekly for at least 4 weeks, then 12.5 mg once weekly for at least 4 weeks, and then 15 mg once weekly as a maximum dose.
If additional glycemic control is needed, you can continue to increase the dose by 2.5-mg increments after at least 4 weeks on the current dose. The maximum dose is 15 mg once weekly.
The 2.5-mg dose is for treatment initiation and is not intended for glycemic control.†
*consider patient history and monitor for tolerability and side effects.
‡Across the five phase 3 SURPASS studies, mean reductions in A1C with Mounjaro ranged from 1.8% to 2.1% for the 5-mg dose, 1.7% to 2.4% for the 10-mg dose, and 1.7% to 2.4% for the 15-mg dose vs 0.1% to 1.9% for comparators. p<0.05 for Mounjaro 5 mg vs study comparators, adjusted for multiplicity.1
Setting Patient Expectations
Tips and resources for you and your staff
Resources for your patients
Digital Starter Kit
Tell your patients to text MJ to 85099 to download a free kit to help them get started on Mounjaro.
The kit provides tips on starting Mounjaro, what to expect, reminder options and additional resources.
Share with your patients how to take Mounjaro with the video below.
[AVO]
Mounjaro is an injectable prescription medicine that is used along with diet and exercise to improve blood sugar (glucose) in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- It is not known if Mounjaro can be used in people who have had pancreatitis.
- Mounjaro is not for use in people with type 1 diabetes.
- It is not known if Mounjaro is safe and effective for use in children under 18 years of age.
Tell your healthcare provider if you get a lump or swelling in your neck, hoarseness, trouble swallowing, or shortness of breath. These may be symptoms of thyroid cancer. In studies with rats, Mounjaro and medicines that work like Mounjaro caused thyroid tumors, including thyroid cancer. It is not known if Mounjaro will cause thyroid tumors, or a type of thyroid cancer called medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) in people. Do not take Mounjaro if you or any of your family have ever had MTC or if you have an endocrine system condition called Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2).
See Indication and Safety Summary with Warnings at the end of this video.
[VO Julia]
[SFX: Light samba music plays.]
Hi there! If you're watching this video, you want to know how to take once-weekly Mounjaro.
I'm going to show you how to store Mounjaro, how to check it before taking it, and the 4 steps for administering your weekly dose.
I'll also talk about how to safely dispose of used Mounjaro pens and the importance of weekly reminders.
Read the Instructions for Use that came with your pen. You can also review the 4 injection steps on Mounjaro.com.
Now, if you're about to start taking once-weekly Mounjaro, you've probably been trying to get those A1C numbers down, like me.
And also, the numbers on the scale... I know that struggle.
That's why my doctor prescribed Mounjaro to help manage my type 2 diabetes by lowering my blood sugar.
Mounjaro is a once-weekly injectable medicine that comes in a single-dose pen.
It's not insulin. And I can take it with or without food.
Mounjaro can cause side effects.
The most common side effects reported by patients were nausea, diarrhea, decreased appetite, indigestion, vomiting, constipation, and stomach pain.
Talk to your doctor about any side effects you have.
And, make sure to stick around for the full Important Safety Information at the end of this video.
Now let's take a closer look at the pen and how to use it.
[SFX: Phone rings.]
And that's my reminder.
I set it so I don't forget to take my weekly dose.
Your reminder style is up to you - the important thing is having one in place.
Because, sometimes the everyday can get overwhelming, right?
Although I can take my dose whenever I want on my scheduled day, I try to take it at the same time.
It may make it easier to know what to do if you miss a dose...
If you DO miss a dose, and it's been less than 4 days (96 hours), take your dose as soon as possible.
You can take your next dose as usual.
If it's been more than 4 days (96 hours), skip that dose.
Administer your next dose on your next regularly scheduled day.
But now I want to help you get familiar with the pen...
This is the base cap - it stays on until right before I inject.
And it's kept in the locked position, too.
There's a clear window, so I can see the medicine.
But where's the needle, you ask? Tucked inside, where I never have to see it.
When it's time to take my weekly dose, I need to double-check a few things first.
It's important to make sure you've got the right medicine and dose and that the medicine hasn't expired. Make sure the pen isn't damaged, too.
I also need to check that the medicine is not frozen, not cloudy, not discolored, and does not have particles.
Now, I have to decide where to inject.
I have options. I can administer it to my belly - at least 2 inches away from the belly button - or the tops of my thighs.
I can also use the back of my upper arms. And if I need it, I can have someone help me inject.
If I want, I can use the same area of my body every week. I just need to make sure not to inject in the exact same spot.
A good guideline is to have your next injection site be at least 1 inch away from your last one.
And right before injecting, I wash my hands.
Then, it's Pull, Place, and Press.
First, when the pen is locked, I pull straight down to remove the gray cap. Throw the cap away and don't ever try to put it back on.
And, don't touch the needle.
Next, I place the base flat against my skin, then unlock.
And, the last step: I press and hold the purple button for up to 10 seconds. The first click means that the injection has started. There's another click when it's done.
I know the injection is complete when the gray plunger is visible.
And... the injection is done!
Always dispose of the used pen in a sharps container. And keep the sharps container in a safe place, away from kids and pets.
Don't ever throw pens in household trash, or recycle the used sharps container.
With the Mounjaro Pen, I can take my once-weekly dose at home, or bring it with me for a last-minute getaway.
The pen can remain at room temperature for up to 21 days. But keep it in its original carton, and out of direct heat and sunlight.
So let's recap: Store your medicine in the fridge, and check it before you take it.
Wash your hands, then follow the 4 steps to administer your weekly dose.
Dispose of the pen safely and make sure you've got a reminder in place for next week's dose.
Getting my blood sugar under control is important to me. That's why my doctor and I decided on Mounjaro.
If you have any questions about treatment with Mounjaro, check out Mounjaro.com, and talk to your doctor.
And don't go away! Stay tuned for the full Important Safety Information.
Thanks for watching! Hon, I'm coming!
Prescribing in your EHR System
Help patients get from initiation to a therapeutic dose of Mounjaro
Select Important Safety Information:
Risk of Thyroid C-cell Tumors: Counsel patients regarding the potential risk for MTC with the use of Mounjaro and inform them of symptoms of thyroid tumors (e.g., a mass in the neck, dysphagia, dyspnea, persistent hoarseness). Routine monitoring of serum calcitonin or using thyroid ultrasound is of uncertain value for early detection of MTC in patients treated with Mounjaro. Such monitoring may increase the risk of unnecessary procedures, due to the low test specificity for serum calcitonin and a high background incidence of thyroid disease. Significantly elevated serum calcitonin values may indicate MTC and patients with MTC usually have calcitonin values >50 ng/L. If serum calcitonin is measured and found to be elevated, the patient should be further evaluated. Patients with thyroid nodules noted on physical examination or neck imaging should also be further evaluated.
References:
- Mounjaro. Instructions for Use. Lilly USA, LLC.
- Mounjaro. Prescribing Information. Lilly USA, LLC.
- Maceira E, Lesar TS, Smith HS. Medication related nausea and vomiting in palliative medicine. Ann Palliat Med. 2012;1(2):161-176.
- Kruger DF, Bode B, Spollett GR. Understanding GLP-1 analogs and enhancing patients success. Diabetes Educ. 2010;36(Suppl 3):44S-72S.
- Reid TS. Practical use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist therapy in primary care. Clin Diabetes. 2013;31(4):148-157

Mounjaro (tirzepatide) is currently only available in a pre-filled single-dose pen manufactured by Lilly. Mounjaro is not commercially available in any other form (e.g., powder for compounding). Products claiming to be compounded Mounjaro (tirzepatide) are not subject to FDA approval and may not have the same safety, quality and efficacy as FDA-approved drugs, and may expose patients to potentially serious health risks.





